Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Mathematics & Physics, Hebei University of Engineering, Handan 056038, China
2 School of Information & Electrical Engineering, Hebei University of Engineering, Handan 056038, China
A high performance optical sensor based on a double compound symmetric gratings (DCSGs) structure is designed. The reflection spectrum of the DCSG is investigated by utilizing a method that combines a theoretical model with the eigenmode information of the grating structure. The theoretical results, which are observed to agree well with those acquired by rigorous coupled-wave analysis, show that the linewidth of the reflection spectrum decreases upon the increasing distance between the grating strips. This research work will lay a foundation for studying high performance integrated optical sensors in miniature nanostructures.
compound gratings sensitivity sensor figure of merit Chinese Optics Letters
2022, 20(2): 021201
1 河北工程大学信息与电气工程学院, 河北 邯郸 056038
2 河北工程大学数理科学与工程学院, 河北 邯郸 056038
导模共振光栅作为一种重要的滤波单元,在光通信中有着广泛的应用。然而,普通的导模共振光栅的传输光谱为洛伦兹型,该类结构在高性能光纤通信系统中的应用受到限制。采用级联导模共振光栅可以实现平顶滤波响应,但是整个器件的体积较大,制作工艺复杂。此外,单一复合光栅结构难以直接实现窄带平顶滤波响应。提出了一种级联双层复合光栅结构以解决这一问题,利用严格耦合波算法和本征模式分析法分析了其输出光谱。仿真结果表明该滤波器的中心波长为1549.9 nm,其平顶光谱的线宽为0.5 nm。
衍射 波长滤波器 导模共振 严格耦合波分析 平顶光谱 复合光栅 光学学报
2021, 41(20): 2005001
1 河北工程大学信息与电气工程学院,河北 邯郸 056038
2 河北工程大学数理科学与工程学院,河北 邯郸 056038
基于导模共振光栅的集成光学滤波器在光纤通信中具有潜在的应用前景,然而单个导模共振光栅的输出光谱一般呈现洛伦兹线型,这会阻碍该类结构在波分复用系统中的应用。传统方法一般采用多个谐振腔级联的方式实现平顶滤波响应,然而整个结构的体积较大,制作工艺较为复杂,因此提出一种基于级联双层导模共振光栅结构,其输出光谱响应为平顶陡边型。首先建立器件的物理模型,其物理机理是将导模共振效应与法布里-珀罗谐振效应结合,然后利用物理模型分析和设计滤波器结构。研究发现该滤波器的中心波长为1550 nm,其3 dB带宽可以增加至20 nm。
光栅 波长滤波器 导模共振 法布里-珀罗谐振腔 平顶光谱 激光与光电子学进展
2021, 58(11): 1105001
1 河北工程大学数理科学与工程学院, 河北 邯郸 056038
2 河北工程大学信息与电气工程学院, 河北 邯郸 056038
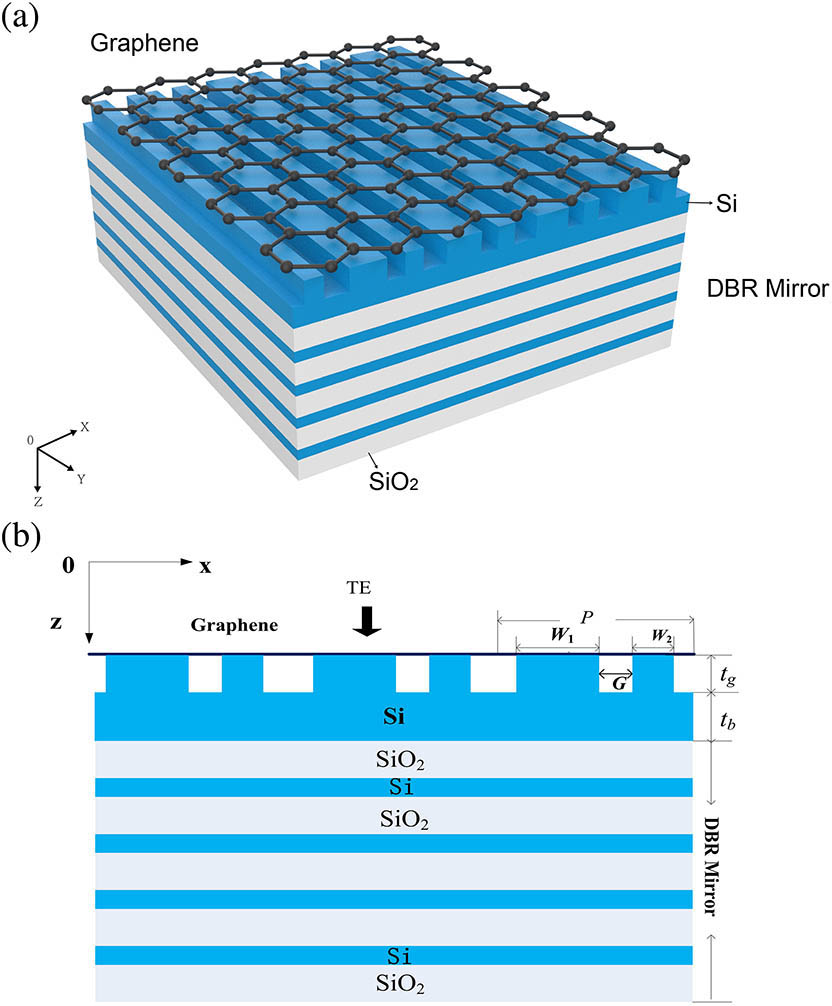
基于导模共振效应的光栅传感器因具有无需荧光标记、易于集成、能实时检测等优点在生物医学传感领域得到了广泛应用。然而,该类型传感器存在品质因子和灵敏度相互制约的问题。为此提出一种凹型光栅结构,也就是在周期性光栅的每一个单元中引入凹型微结构,增强光场与检测物质的相互作用,进而提升传感器的品质因数。利用严格耦合波算法设计了器件结构,分析器件的本征模式,阐明其物理机理。仿真结果表明,该器件的品质因数可达到6562.5。本研究工作将为研制基于微纳结构的高性能集成光学传感器提供研究基础。
集成光学 集成光学传感器 品质因数 导模共振光栅 严格耦合波分析
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Information & Electrical Engineering, Hebei University of Engineering, Handan 056038, China
2 School of Mathematics & Physics, Hebei University of Engineering, Handan 056038, China
3 State Key Laboratory of Information Photonics and Optical Communications, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Beijing 100876, China
We present a perfect graphene absorber with a compound waveguide grating at the near-infrared. The analytical approach is mainly based on the coupled leaky mode theory, which turns the design of the absorber to finding out the required leaky modes supported by the grating structure. Perfect absorption occurs only when the radiative loss of the leaky mode matches the intrinsic absorption loss, which is also named the critical coupling condition. Furthermore, we also demonstrate that the critical coupling of the system can be robustly controlled, and the perfect absorption wavelength can be easily tuned by adjusting the parameters of the compound waveguide grating.
050.6624 Subwavelength structures 140.4780 Optical resonators Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(1): 010501

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 The School of Information & Electrical Engineering, Hebei University of Engineering, Handan 056038, China
2 The School of Mathematics & Physics, Hebei University of Engineering, Handan 056038, China
3 College of Science, Zhejiang University of Technology, Hangzhou 310023, China
An optical sensor is designed to support the Fano effect based on a compound resonant waveguide grating (CRWG). The transmission spectra of the CRWG are investigated by utilizing a theoretical method that combines the temporal coupled mode theory with the eigenmode information of the grating structure. The theoretical results, which are observed to agree closely with those acquired by rigorous coupled-wave analysis, show that the linewidth of the transmission spectrum decreases upon increasing the distance between the grating strips, and the central resonance frequency decreases as the refractive index of the analyte increases. Here, the proposed CRWG structures will find potential uses in optical sensing.
050.6624 Subwavelength structures 130.6010 Sensors Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(3): 030502
1 河北工程大学信息与电气工程学院, 河北 邯郸 056038
2 光纤通信与宽带接入技术邯郸市重点实验室, 河北 邯郸 056038
3 河北工程大学理学院, 河北 邯郸 056038
4 北京邮电大学信息光子学与光通信国家重点实验室, 北京 100876
为了便于理解亚波长高折射率差光栅的谐振滤波机制,将光栅看作一个光学谐振器,用时域耦合模理论分析光栅滤波器的透射光谱,同时也验证了分析结果与严格耦合波算法仿真结果的一致性。在此基础上,分别分析入射角、光栅宽度以及温度对光栅滤波器的透射特性的影响及机理。研究结果表明通过改变入射角可以调控光栅滤波器透射光谱的线宽,而在小范围内改变光栅宽度和工作温度对透射光谱线宽没有影响。
光栅 亚波长光栅 光滤波器 谐振器 时域耦合模理论 激光与光电子学进展
2016, 53(5): 050502
1 江西农业大学生物光电技术及应用重点实验室, 江西 南昌 330045
2 江西出入境检验检疫局综合技术中心, 江西 南昌 330038
采用激光诱导击穿光谱(LIBS)技术对大豆油中的铬(Cr)含量进行检测研究。以一系列Cr 含量不同的大豆油为样本,采用AvaSpec 双通道高精度光谱仪在206.28~481.77 nm 波段范围内采集LIBS 光谱。根据样本的LIBS 谱线图,确定Cr 元素的主要特征谱线,并对Cr 元素主要特征谱线应用线性回归或最小二乘支持向量机(LS-SVM)方法建立其单变量、二变量及多变量校正模型。利用建立的校正模型对样本Cr 含量进行预测。研究结果表明,二变量及多变量校正模型的性能优于单变量校正模型,LS-SVM 建立的多变量校正模型性能最优。对于单变量及二变量校正模型,预测样本的平均相对误差(RE)分别为14.16%和11.58%;而对于线性回归及LS-SVM 建立的多变量校正模型,预测样本的平均RE 分别为10.95%和4.97%。由此可见,LIBS 技术检测大豆油中的重金属Cr 含量具有一定的可行性,LS-SVM 方法可以有效提高校正模型的预测精度。
光谱学 激光诱导击穿光谱 大豆油 铬含量 最小二乘支持向量机 激光与光电子学进展
2016, 53(4): 043001
天津亿利科能源科技发展股份有限公司, 天津 300384
油气管线内部腐蚀是导致管线失效的主要因素。针对这一问题,采用复用技术设计了一种基于光纤布拉格光栅的管线内腐蚀监测系统。该系统通过出地管线外表面的应力变化来确定内表面的腐蚀程度,利用7路光纤光栅传感器组成阵列式传感网络,通过温度补偿光栅实现温度补偿。实验表明,该系统测压精度较高,系统误差小于2.23%。用现场实际压力数据验证了系统的可行性与稳定性,该系统完全满足油气管线内部缺陷在线监测的要求。
光纤光学 管道腐蚀 布拉格光纤光栅 复用技术 温度补偿 激光与光电子学进展
2014, 51(2): 020604





